Bariatric Surgery, weight loss surgery

The weight loss surgery, also called bariatric surgery, is currently the most effective treatment for severe obesity in terms of magnitude and duration of weight loss. The extent to which obesity decreases the quality of life like health should not be underestimated.
Bariatric surgery can result in loss of 45% to 80% of excess body weight ideal weight according to the individual. It is common to diet or exercise can lose up to 10% of excess body weight with ease, it is difficult to maintain this weight loss or continue to lose weight. It is in these patients where surgery for obesity shows its greatest benefits.
Have you failed trying to reduce weight through diet and exercise?

A healthy diet , exercise and changes in lifestyle are appropriate measures to reduce weight . This includes eating moderate amounts of foods rich in nutrients, low in fat and calories and add more physical activity into the day. To achieve this requires a change in thinking , feeling and acting .
While a healthy diet and an exercise routine can result in weight loss, the real challenge is to keep the weight has been reduced. Unfortunately, studies show that almost 100 % of obese patients undergoing diet to reduce weight , fail to maintain it within a period of 5 years. Worse, a continuous cycle of weight loss and gain can cause serious health problems.
If you have tried to reduce weight through diet and exercise , but remains an obese person , the weight loss surgery ( bariatric surgery ) may be the best way to restore your health.
Who is a candidate for Bariatric Surgery?
• People who are 100 pounds over their ideal weight
• People with a BMI greater than or equal to 40
• People with higher BMI of 35 or more co-morbidities
How Effective is Bariatric Surgery?
The weight loss after the procedure will depend on several factors , these include :
• Age of the patient.
• Weight before surgery .
• General condition of patient health.
• type of surgery performed.
• Ability of the patient to perform exercises.
• Commitment to maintain patient treatment, dietary guidelines and monitoring.
• Motivation of patient and cooperation of family , friends and associates.
Recent studies have shown that the success of bariatric surgery is defined as the ability to achieve and maintain the loss of at least 50 % of excess body weight without adverse effects. Clinical data show that the results vary depending on the procedure performed and the operating surgeon .
Patients may lose 35 to 40 pounds in the first 4 weeks after surgery , 30% to 50 % of excess body weight in the first 6 months and up to 77% of excess body weight at their first year . Furthermore, studies have shown the ability to maintain 50% to 60 % of the total weight loss beyond 10 years after surgery .
It is noteworthy that patients with higher baseline BMI, tend to lose as many pounds, while patients with lower BMI lose the highest percentage of overweight, approaching this way to your ideal weight.
Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 tend to lose less weight than non-diabetic patients, but numbers studies have shown remarkable improvement in the control of diabetes, and in some, complete resolution of diabetes, to the point, no need to continue to take your medicine.
Bariatric surgery has proven effective for improving and controlling many obesity-related diseases. A clinical analysis involving 22,000 patients showed that bariatric surgery patients experienced an improvement in their comorbid condition in diabetes, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, musculoskeletal disorders and sleep apnea.
Open or laparoscopic surgery?
Bariatric surgery can be performed in two ways:
The laparoscopic procedure is performed by making a tiny incision in the abdominal wall. A small video camera is inserted by these incisions allowing the surgeon to observe the procedure for monitor. Thin instruments used to perform the surgery are inserted through the other incisions remaining. Other cuts besides the mention are not required to complete the procedure. It is for this reason that laparoscopic surgery is considered “minimally invasive” compared with open surgery. Patients who had undergone laparoscopic gastric bypass refer to experience less pain and greater ease in breathing that those who have undergone the same procedure by open surgery.
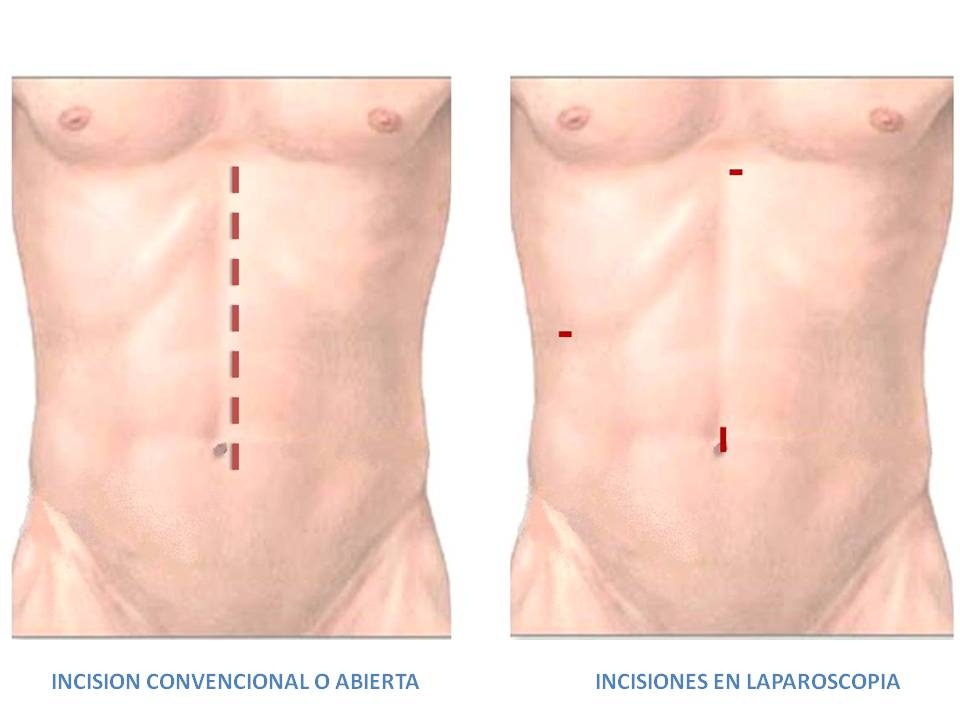
Open surgery is a single, vertical incision in the center of the abdominal wall. The size of this may vary depending on the surgeon, but it must be large enough to allow this to visualize the stomach and perform the procedure. Open surgery usually requires a longer hospital stay than laparoscopic surgery.
What if the surgery can not be performed laparoscopically?
In a minority of patients, the laparoscopic procedure is not working effectively. Factors that may increase the possibility of choosing or converting to open surgery procedure include:
– Obesity
– History of previous abdominal surgery by dense scar tissue
– Inability to visualize organs
– Bleeding problems during surgery
What are the results of bariatric surgery?
As bariatric surgery continues to grow and develop, clinical data have yielded numerous benefits. In contrast to the usual treatments for obesity, at least two thirds of patients who undergo weight loss surgery are able to reduce at least 50% of their excess weight over the next ten years or more. Surgery to reduce weight has shown a dramatic influence on the increase in life expectancy. The co-morbidities such as sleep apnea and hypertension, are reduced, but eliminated after surgery.
 Surgical treatment, despite its risks, treatment is most effective long-term extreme obesity, when all other therapies have failed. The surgical modality for the treatment of obesity is continually gaining ground and more patients who come to her because of the high incidence of obesity today.
Surgical treatment, despite its risks, treatment is most effective long-term extreme obesity, when all other therapies have failed. The surgical modality for the treatment of obesity is continually gaining ground and more patients who come to her because of the high incidence of obesity today.
The weight that the patient may lose depends on your age, your weight before surgery, general health, physical activity or ability to perform exercises and follow the diet.
What are the risks of bariatric surgery?
Like any surgical procedure, bariatric surgery also has its risks. Please consult your doctor what would be the right treatment for you. It is important that you ask your surgeon what are the specific risks that could present you depending on your health condition and what the specific procedure to follow.
Potential Postsurgical Complications
One or all of the following conditions and complications can occur in any of the surgical procedures discussed above, as well as any type of gastric surgery:
Potentially serious surgical complications:
• Surgical: perforation of the stomach / intestine or líqueo, causing peritonitis or abscess. Internal bleeding may require transfusion. Wound infection, this opening, incisional hernia. Splenic injury that could require the removal or damage to any other body. Gastric outlet obstruction or bowel obstruction.
• Pulmonary: Pneumonia – atelectasis (collapse of lung tissue), fluid in the lungs. Respiratory failure, pulmonary edema. Thromboembolism (blood clots in legs / lungs).
• Cardiovascular: Cardiac Infarction – congestive heart failure. Arrhythmias. Strokes.
• Kidney and Liver (Kidney / Liver): Acute renal failure. Liver failure – hepatitis (may progress to cirrhosis).
• Psychosocial: Anorexia-Bulimia nervosa. Postoperative depression, social problems. Psycho.
• Death
Other complications (may be serious):
• Minor wound infections or skin.
• Urinary tract infections.
• Allergic reactions to drugs or medication.
• Vomiting or nausea.
• Difficulty eating certain foods or improper diet.
• Inflammation of the esophagus, heartburn.
• Low concentration of sodium, potassium or glucose can cause hypotension.
• Anemia, metabolic deficiency (iron, vitamins, minerals)
• Temporary loss of hair.
• Constipation, diarrhea, flatulence (gas), cramping, malodorous stools.
• Formation of stones in the gallbladder.
• Ulcers gastric outlet (peptic ulcer).
• Discontinuity of the line of sutures.
• Weight gain – not get satisfactory weight loss.
• Penetration of surgical material or ulceration (gastric band and rings) into the stomach.
• refined sugar intolerance (dumping), nausea, sweating and general weakness.
Important Considerations
Surgery should not be considered until you and your doctor have not considered all the other options. The proper approach to surgery to reduce weight requires careful consideration and discussion with your doctor the following:
• Surgery to reduce weight in no circumstances should be considered as cosmetic surgery. The procedures do not involve cutting or fat suction .
• The decision to elect surgical treatment requires an analysis of the risks and benefits to the patient and meticulous implementation of an appropriate surgical procedure.
• Surgical procedures to reduce weight are irreversible.
• The outcome of surgery to reduce weight depends on the lifestyle changes the patient’s long-term diet and exercise.
• Can complications after surgery that may require reoperation arise.
The decision to have this surgery must be done after careful consultation with an experienced bariatric surgeon or a known family physician.
Before being approved for bariatric surgery, you must:
• Show that you are seriously motivated and interested in losing weight.
• clearly understand the risks of surgery.
• Be prepared to make a lifetime commitment by conducting strict diet, exercise and medical care.
Preparing for operation
Before the procedure you will have passed through a series of assessments, labs and studios, however, you must put your surgeon aware of any health problems you have. You must report all medications you use, it is important that the surgeon is aware of these.
Laboratory Tests:
- CBC
- erythrosedimentation
- urine
- RH typing
- glycemia
- Glycated
- And TP TPT
- creatinine
- urea
- Total cholesterol
- triglycerides
- Lipid Profile
- SGOT
- SGPT
- Alkaline Phosphatase
- GGTP
- Total proteins
- albumin
- amylase
- lipase
- sodium
- potassium
- chlorine
- calcium
- Pregnancy Test
- HIV
- HBsAg
- HCV
- Helicobacter pylori
- T3, T4, TSH
Guide for preoperative preparation:
1. Seeing a Psychologist
Two. Laboratories or blood tests
Three. Imaging Studies – scan of chest and abdomen
April. Collect the results of laboratory and imaging studies
May. Consultation with cardiologist – pre-operative evaluation
6. Seeing a specialist Sleep Apnea
7. Seeing a Gastroenterologist – Upper GI Endoscopy and Biopsy
8. Consultation with Endocrinologist
9. Bringing the results of the studies and by employees to set the day of surgery
NOTE: It is important to do these steps in the order described and duly listed. Some doctors and laboratory studies needed to make their assessments.
You will meet the anesthesiologist prior to the procedure. You need to communicate accurately if you are allergic to any medications, if you have a neurological disorder, if you have heart, if you have stomach problems if you have lung problems (asthma or emphysema), if you have any endocrine disorders (diabetes or thyroid), if you have lost a tooth, if you smoke, drink alcohol, or use drugs.
What questions should you ask before surgery?
• What medications should I leave or stay?
• When should I for these drugs and for how long?
• What type of anesthesia will use me, what are my options?
• What are the risks and complications of general anesthesia?
• Do I need to take antibiotics before surgery?
• What should I do to prevent thromboembolism?
The day of surgery
DO NOT EAT OR DRINK
Do not eat or drink at least 12 hours before your surgery, you must take into account that when ingesting food or liquid puts your health at risk, since at the time of anesthesia reflexes are lost and vomiting and aspiration can happen intestinal contents into the lungs, this is a fatal complication. Besides surgery is in the digestive tract so that the same clean and free this food waste is required.
What should you have with you?:
• Your ID or identification.
• Analytical and previous studies (all evaluations performed before)
• Cardiologist Authorization (required for anesthesia)
• List of medications and drugs you use.
• Personal items such as eyeglasses and dentures.
• Clothing and shoes.
• Leave clothes and valuables at home.
At the time of placement
On admission he placed an intravenous catheter with a solution to hydrate and administering medications ; Some drugs make you sleepy . It is common medications administered to protect the stomach and prophylactic antibiotics (to prevent infection).
In the operating room, the anesthesiologist will administer medication to dormirlo , then place a tube in your throat to administer anesthetics during surgery.
The surgeon will perform the operation and eventually close the incisions ; must leave a drainage tube , except in cases of gastric banding . After surgery, it will remain in the recovery area around one to three hours .
Recovery and discharge
After the surgery will be a few hours with the anesthetic effects , it is often not remember the first moments upon waking. These effects gradually disappear , some people can last more than 48 hours. By the time of discharge is likely to feel recovered. In-hospital time varies between 24 to 72 hours.
Nutrition

Waking once have passed anesthesia , will remain without food for a period of 24 to 36 hours , then once is restored peristalsis (bowel movements ) was performed imaging studies using contrast media to confirm that there are no leaks in the lines of sutures, and to confirm the position of the device in the case of adjustable gastric band , then start fluid tolerance will , it is to eat small amounts of liquid . If not ensue nausea or vomiting, then the liquid diet as instructed continues. Then it is recommended to maintain adequate hydration eating at least 2 ounces of fluid every 15 to 30 minutes. Recalling that the capacity of the stomach is reduced and hence oral hydration should be constant and in small amounts.
The intake of solids will be suspended for several weeks, it is common for changes in the pattern evacuatorio . Constipation or constipation is common for the lack of intestinal motility. Some pain medications can cause constipation. To manage this condition diet high in fiber or adding fiber to the diet , sometimes the use of laxatives is necessary is recommended.
Foods high in fiber include beans , grains , cereals , wholemeal bread , dried fruits , sweet corn , broccoli , pear, apple , peach , papaya and nuts. These can be added to the liquid broth without strain or juices.
Physical Activity

It is recommended to stay out of bed as long as possible , sitting or lying down is better than wandering . Gradually should increase their physical activity , however , we recommend no heavy lifting or strenuous activity during the first 4 weeks in cases of laparoscopic surgery, and at least 12 weeks in cases of open surgery.
You can perform any type of activity that your body will allow , as long as no pain without the use of pain medication , avoid driving or operating heavy machinery .
You can resume sexual activity once you feel in the mood to do , do it with prudence and moderation , avoid hurting wounds.
It is normal to feel exhausted or sleepy , you will notice that you need to sleep more than usual , this is normal and usually improves with every passing day. Sometimes this is associated with lethargy, dehydration or hypoglycemia so the best should stay hydrated as possible. Avoid walking in pajamas all day , try to integrate into daily activities as your body will allow.
work
You can work once you feel better , this may vary in patients. Laparoscopic surgery allows early entry into the daily work , usually patients who undergo a laparoscopic procedure return to work in the first week . In cases of open surgery is required between 3 and 4 weeks, sometimes it requires more time .
Wound Care
You must follow the instructions to the letter when it comes to wound care .
You should wash your hands before touching near the wounds .
In most cases use dermabond ( skin adhesive ) , this works as sterile dressing is waterproof and does not permit the passage of bacteria . If this product is used on your wound , you can bathe comfortably and wet their wounds.
When we use steri strips ( tapes sterile ) , is allowed to bathe in the second postoperative day . You can wet their wounds and is recommended not to remove the tapes , you better expect to fall alone. The steri strips regularly fall alone at 7 or 10 days.
In the event that you have in your wounds sterile dressings ( bandages , dressings or bandages ) not to touch these dressings until you order , sometimes the wound should be kept covered for several days. You should wait for these dressings are removed to wash his wounds.
Sometimes it is normal to see some liquid goes through his wounds, if it is yellow, amber or orange, there is nothing to fear ; If the drainage becomes thick and white , you should tell your doctor , the infection is usually accompanied by redness and swelling of the area.
If you have placed a drain in one of the incisions , this will be removed when no more liquid comes out through the drain, the time for this to happen may vary.
For most procedures , we use internal points , it is likely that you will not withdraw sutures. In cases where the skin with stitches or staples outside , these will be removed in a second date , whether the wounds are healed sutured .
Avoid wearing tight or uncomfortable , avoid rubbing the wound as this can cause injury and delayed healing .
Protect wounds, especially the Sun, this can cause thickening and darkening of the wounds . Use sunscreens to enhance the aesthetic results .
His wounds healed in about 6-8 weeks you will gradually disappear and skin tightening will be more smooth and clear . The process of healing and skin remodeling lasts about a year. The sensitivity around the wounds take weeks or months to improve.
Pain
The perception and pain intensity varies in people. Usually the pain is quite tolerable in minimally invasive surgery , even without the use of drugs. For some patients need two to three daily doses of analgesics ( pain medications ) , while in others the use of narcotics is necessary.
It is important to note that pain medications tend to irritate the stomach and this is not good for patients with gastric surgery, if pain is tolerable , the use of analgesics should be avoided. In patients with gastric restriction analgesics are administered as syrup , syrups contain sugar and this can affect weight loss .
Each person reacts differently to pain . Pain measurement scales are used to determine the degree of pain , this scale is from 0 to 10 . Given value of 0 when there is no pain and 10 the pain but he has received in his life.
Drugs
• For pain control :
No narcotics – this group is composed mainly of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs ) are the most widely used postoperatively for control of mild to severe pain . These also decrease inflammation . Some of the unwanted effects is irritation of the stomach ( gastritis) , bowel irritation and fluid retention . These effects are only seen with prolonged use . These drugs have ibuprofen , diclofenac , naproxen, meloxicam and others.
Narcotics or opioids – are regularly used to control severe pain. Some of the unwanted effects of narcotics are drowsiness , lethargy , decreased blood pressure , heart rate and respiratory rate , itching and skin irritation , constipation , nausea , difficulty urinating . Examples of these include morphine, oxycodone and hydromorphone . There are drugs to control the side effects of narcotics .
After a laparoscopic procedure is common sense discomfort or pain in the shoulder, this is due to the irritation caused by the gas used in the abdomen during surgery, Walking and moving help lower gas within the abdomen and therefore improves pain .
• Antibiotics
in most cases antibiotic prophylaxis ( prevention ) is used . Antibiotic dose of one or half hour before surgery applies . Where the process is advanced appendiceal need more than 2 days of hospitalization for antibiotics , it is common to use several in combination.
Antibiotic prescribing for the house is very important and depends on the findings at surgery and consider what your doctor for your particular case.
You should contact your surgeon if you:
• you have severe pain that does not improve with medication .
• Feel the pain has worsened with the passing of the hours.
• Note that the pain is accompanied by fever higher than 38.5 ° C.
• develop nausea or vomiting.
• Notes that the wounds are wet , red or have pus.
• Severe pain of new onset .
• No bowel movements or feel bloated.
• No gases discharged or spend more than three days.
