Gallbladder
The gallbladder is an organ located beneath the liver and looks like a small pear -shaped pouch . The liver produces about 3-5 cups daily bile , bile is produced in the gallbladder , this serves to store and concentrate , and when food is ingested, especially those containing fat, the gallbladder contracts and squeezes its contents draining through the cystic duct and common bile duct to the small intestine .
Medically we call gallstones , the formation of calculi (stones ) in the gallbladder. We call these formations choledocholithiasis when present in the common duct. The stones within the ducts can cause obstruction to the flow of bile and thus pain, inflammation and infection.
Most people have no symptoms calculations , it is common that the patient is aware of this condition incidentally becoming routine sonography or some other cause , many patients go for years with stones in the bile duct without evidence of alteration.
It is common to see stones in people who :
• Have a family history of stones in the bile duct
• Are overweight
• Eat high sugar content
• Are pregnant
• do not exercise regularly
• Lose Weight Fast
• They use estrogen for menopause
Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder and this may occur suddenly (acute) or gradually over a long period of time ( chronic) . The gallbladder may have different degrees of inflammation that can range from mild to severe , sometimes even can get drilled and seriously complicated.
The pain of the gallbladder is located in the right upper quadrant is colicky , ie improves or disappears at times and is most intense at times , its duration is variable and is related to food intake with high fat content .
In acute cholecystitis pain usually lasts more than 6 hours and no abdominal rigidity and irritability , this may or may not be accompanied by fever, other possibilities must be ruled pain in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen , such as ulcers , liver problems or heart . The treatment of acute inflammation of the gallbladder is aimed at reducing symptoms of inflammation with antibiotics and anti-inflammatories to subsequent cholecystectomy.
Symptoms
The most common symptoms of cholecystitis are:
• severe intermittent pain in the upper right side of the abdomen .
• Mild to moderate fever
• Nausea and Indigestion
• Jaundice (yellowing of the skin) may occur when the calculations are found in the common duct.
Research and Laboratories
Abdominal ultrasound or sonography , this is a test that uses sound waves that travel through the body and create images of internal organs. This is a quick , simple study and does not produce any pain. It is the most common study and more effective in detecting stones in the gallbladder. Sometimes the patient is asked to remain fasting performed the study.
Blood Tests
• CBC (complete blood count )
• Liver function tests
• Tests of blood coagulation
• Textual pancreatic
• Kidney Tests
• Textual Viral
Other studies
• HIDA Scan
• Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiography
• Magnetic Resonance
• Cholangiopancreatography
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is recommended for pain gallbladder stones treatment , and is the only treatment for acute cholecystitis.
Cholecystectomy is the surgical procedure by which the removal of the gallbladder is done . The most common cause or reason for this surgery is when the gallbladder has stones in it or when it is inflamed or infected , causing colicky pain (sudden abdominal pain caused by spasm or blockage of the bile duct ) .
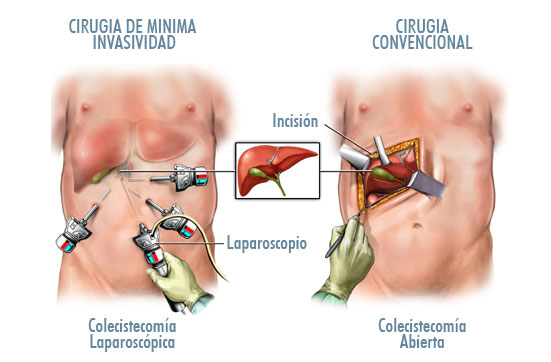
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy
This technique is the most common for simple cholecystectomy in most developed countries. The surgeon makes four small incisions ( 0.5 to 1 cm ) in the abdomen through which thin tubes or cannulas (ports ) where carbon dioxide, a gas used to inflate the abdomen and create space is entered are inserted . This process allows the surgeon to visualize the gall bladder and the remainder of the abdominal cavity with ease .
A laparoscope ( or tubular cylindrical lens which is connected to a video camera and light source) is introduced through another port . This allows the surgeon to see inside the abdomen on a screen or monitor. Then specialized instruments are inserted through other ports for dissection and removal of the gallbladder.
The surgeon removes the gallbladder through an incision , the carbon dioxide is removed from the abdominal cavity through the ports , then these are closed with sutures . The surgery usually lasts between 30 minutes and 1 hour.
The surgeon can start laparoscopic surgery or minimally invasive manner and conversion to conventional open surgery or if technical difficulties may be necessary to perform the procedure or the patient’s own anatomical variants . The cup conversion in young people without underlying diseases is less than 1 %.
The need for conversion occurs mainly when :
• The patient has experienced several episodes of acute pain (acute cholecystitis)
• Have previous abdominal surgery with large incisions.
• If you are over 65 years old.
• have a high fever .
• Have high bilirubin.
• Has limiting illnesses.
Open cholecystectomy
The surgeon makes an incision approximately 15 cm long under the ribs in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen , cutting through fatty tissue, fascia and muscle to reach the abdominal cavity exposing the gallbladder. Just as laparoscopy in gallbladder and liver ducts and blood vessels are removed or tied closed with sutures.
The wound is closed in layers with sutures and sometimes a drain is left from the internal to the external abdomen. The drain is usually removed during detention. This procedure usually takes between 1 and 2 hours.
Risks of this operation
• Infection – this occurs in less than 0.1% of the operated patients .
• Injury to the common bile duct – it is reported that only 0.1 % for patients with open surgery and 0.2 % for laparoscopic surgery.
• Bleeding – bleeding is rare in patients with chronic liver disease coagulation factors often altered , the bleeding may be slightly higher in the open surgery because the incision.
• Líqueo bile – is rare.
• Retained stones in the common rail – it may be the case that a rock pass to the common duct and obstruct drainage of bile .
• Pneumonia – can be seen in any surgery under general anesthesia or surgeries that limit respiratory movements ( open cholecystectomy ) and ambulation .
• Heart Problems – these are very rare .
• Kidney problems – have been reported in 0.5 % of patients and is usually due to dehydration or liver disorders .
• Deep vein thrombosis – the absence of movement during surgery can lead to blood clots in the legs , clots can move and stay in the lungs. This decreases with laparoscopy enough as it is outpatient surgery and the patient remains in bed shortly .
• Premature labor or fetal loss – the loss or fetal death seen in 4% of pregnant patients with uncomplicated cholecystectomy and can be as high as 60 % in cases of pancreatitis accompanying or in cases there peritonitis .
• Abdominal organs or intestinal injury – surgical instrumentation can damage internal organs the surgeon should have experience and caution , making sure any sign of injury to organs or obese patients with previous surgeries are more difficult to operate.
• Death – is extremely rare for this disease and is reported to be 0.01 % , is seen in patients with local gangrene, advanced infection , sepsis or concomitant diseases.
Preparing for operation
You must put your surgeon aware of any health problems you have. Please bring a list of all medications you use, it is important that the surgeon and anesthesiologist are aware of these .
In most cases it is recommended not to suspend their usual treatments, except for anticoagulants and antiplatelet ( plavix , coumadin or aspirin ) which must be stopped , it is recommended that in the morning the drugs are taken with small amount of liquid. If hypertensive You should take your medication as usual .
You will meet the anesthesiologist on the day of the procedure. You need to communicate accurately if you are allergic to any medications, if you have a neurological disorder , if you have heart , if you have stomach problems if you have lung problems ( asthma or emphysema) , if you have any endocrine disorders (diabetes or thyroid), if you have lost a tooth , if you smoke , drink alcohol or use drugs .
What questions should you ask before surgery?
• What medications should I leave or stay?
• When should I for these drugs and for how long?
• What medicines should I take the day of surgery?
• What are the risks and complications of general anesthesia?
• Do I need to take antibiotics before surgery?
• What should I do to prevent thromboembolism?
• Should I shave the area of the surgery and how?
The day of surgery
DO NOT EAT OR DRINK
Do not eat or drink at least 6 hours before your surgery , you must take into account that when ingesting food or liquid puts your health at risk , since at the time of anesthesia reflexes are lost and vomiting and aspiration can happen intestinal contents into the lungs , this is a fatal complication.
What to bring with you:
• Your insurance card .
• Authorization of insurance.
• Your ID or identification.
• Analytical and previous studies .
• Authorization Cardiologist .
• List of medications and drugs you use.
• Personal items such as eyeglasses and dentures.
• Clothing and shoes .
• Leave clothes and valuables at home.
At the time of placement
On admission he placed an intravenous catheter with a solution to hydrate and administering medications ; Some drugs make you sleepy . It is common medications administered to protect the stomach and prophylactic antibiotics (to prevent infection).
In the operating room, the anesthesiologist will administer medication to dormirlo , then place a tube in your throat to administer anesthetics during surgery.
The surgeon will perform the operation and eventually close the incisions , sometimes it is necessary to leave some sort of drainage. After surgery, it will remain in the recovery area for about an hour .
Recovery and discharge
After the surgery will be a few hours with the anesthetic effects , it is often not remember the first moments upon waking. These effects gradually disappear , some people can last more than 48 hours, during this period you should avoid driving , operating heavy machinery , drink alcohol or take important decisions .
Nutrition
Waking once they have passed the anesthesia , you will start to tolerance of liquid , this liquid is ingested in small amounts. If not ensue nausea or vomiting, then the current diet is started. Then it is recommended to maintain adequate hydration eating at least 8 to 10 glasses of water per day.
Some surgeries evacuatorio produce changes in the pattern. Constipation or constipation is common for the lack of intestinal motility. Some pain medications can cause constipation. To manage this condition diet high in fiber or adding fiber to the diet , sometimes the use of laxatives is necessary is recommended.
Foods high in fiber include beans , grains , cereals , wholemeal bread , dried fruits , sweet corn , broccoli , baked potatoes with peel , pear, apple , peach, milky and nuts.
In the post cholecystectomy patients is important to remember that foods high in fat cause diarrhea , it should avoid fried foods or foods with oils high in fat. Also, when it comes to bowel diarrhea is common procedures , if it is maintained beyond the third day, ask your doctor .
Physical Activity
It is recommended to stay out of bed as long as possible , sitting or lying down is better than wandering . Gradually should increase their physical activity , however , we recommend no heavy lifting or strenuous activity for the first week in cases of laparoscopic surgery, and at least for 3 weeks in cases of open surgery.
You can perform any type of activity that your body will allow , as long as no pain without the use of pain medication , avoid driving or operating heavy machinery .
You can resume sexual activity once sitting with the intention to do so , do so with caution and restraint , avoid hurting wounds.
It is normal to feel exhausted or sleepy , you will notice that you need to sleep more than usual , this is normal and usually improves with every passing day. Avoid walking in pajamas all day , try to integrate into daily activities as your body will allow.
Work
You can work once you feel better , this may vary in patients. Laparoscopic surgery allows early entry into the daily work , usually patients who undergo a laparoscopic procedure return to work in the first week . In cases of open surgery is required between 3 and 4 weeks, sometimes it requires more time .
Wound Care
You must follow the instructions to the letter when it comes to wound care .
You should wash your hands before touching near the wounds .
In most cases use dermabond ( skin adhesive ) , this works as sterile dressing is waterproof and does not permit the passage of bacteria . If this product is used on your wound , you can bathe comfortably and wet their wounds.
When we use steri strips ( tapes sterile ) , is allowed to bathe in the second postoperative day . You can wet their wounds and is recommended not to remove the tapes , you better expect to fall alone. The steri strips regularly fall alone at 7 or 10 days.
In the event that you have in your wounds sterile dressings ( bandages , dressings or bandages ) not to touch these dressings until you order , sometimes the wound should be kept covered for several days. You should wait for these dressings are removed to wash his wounds.
Sometimes it is normal to see some liquid goes through his wounds, if it is yellow, amber or orange, there is nothing to fear ; If the drainage becomes thick and white , you should tell your doctor , the infection is usually accompanied by redness and swelling of the area.
If you have placed a drain in one of the incisions , this will be removed when no more liquid comes out through the drain, the time for this to happen may vary.
For most procedures , we use internal points , it is likely that you will not withdraw sutures. In cases where the skin with stitches or staples outside , these will be removed in a second date , whether the wounds are healed sutured .
Avoid wearing tight or uncomfortable , avoid rubbing the wound as this can cause injury and delayed healing .
Protect wounds, especially the Sun, this can cause thickening and darkening of the wounds . Use sunscreens to enhance the aesthetic results .
His wounds healed in about 6-8 weeks you will gradually disappear and skin tightening will be more smooth and clear . The process of healing and skin remodeling lasts about a year. The sensitivity around the wounds take weeks or months to improve.
Pain
The perception and pain intensity varies in people. Usually the pain is quite tolerable in minimally invasive surgery , even without the use of drugs. For some patients need two to three daily doses of analgesics ( pain medications ) , while in others the use of narcotics is necessary.
Each person reacts differently to pain . Pain measurement scales are used to determine the degree of pain , this scale is from 0 to 10 . Given value of 0 when there is no pain and 10 the pain but he has received in his life.
Drugs
For pain control :
No narcotics – this group is composed mainly of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs ) are the most widely used postoperatively for control of mild to severe pain . These also decrease inflammation . Some of the unwanted effects is irritation of the stomach ( gastritis) , bowel irritation and fluid retention . These effects are only seen with prolonged use . These drugs have ibuprofen , diclofenac , naproxen, meloxicam and others.
Narcotics or opioids – are regularly used to control severe pain. Some of the unwanted effects of narcotics are drowsiness , lethargy , decreased blood pressure , heart rate and respiratory rate , itching and skin irritation , constipation , nausea , difficulty urinating . Examples of these include morphine, oxycodone and hydromorphone . There are drugs to control the side effects of narcotics .
Antibiotics
In most cases antibiotic prophylaxis ( prevention ) is used . Antibiotic dose of one or half hour before surgery applies . It’s unusual prescription of antibiotics to the house, this will depend on the findings at surgery and consider what your doctor for your particular case.
You should contact your surgeon if you:
• you have severe pain that does not improve with medication.
• Feel the pain has worsened with the passing of the hours.
• Note that the pain is accompanied by fever higher than 38.5 ° C.
• develop nausea or vomiting.
• Notes that the wounds are wet, red or have pus.
• Note that your skin looks yellow (jaundice).
• No bowel movements or feel bloated.
• Have watery diarrhea for more than three days.

Download Brochure(spanish only)
